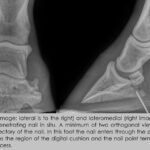
Laminitis, or founder, is the inflammation and damage to the laminae in the hoof of animals like horses or cows, often triggered by poor diet, obesity, or inflammatory diseases. Anti-inflammatory drugs play a crucial role in managing this painful condition by reducing inflammation and alleviating pain, improving the animal’s comfort and recovery.
How Do Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Help with Laminitis?
Anti-inflammatory drugs, particularly NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), are commonly used in treating laminitis because they inhibit the production of prostaglandins, which are key mediators of inflammation and pain. By reducing prostaglandin synthesis, NSAIDs help to decrease inflammation in the hoof, alleviate pain, and improve blood flow, thus aiding the healing process.
What Types of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Are Used?
NSAIDs are the primary anti-inflammatory drugs used to manage laminitis. Examples include:
- Ibuprofen: Effective for mild to moderate pain and inflammation.
- Naproxen: Similar to ibuprofen, providing relief from pain and inflammation.
- Ketoprofen: Another option for managing pain and inflammation associated with laminitis.
- Aspirin: While technically an NSAID, it is used less commonly due to potential side effects and the availability of newer, more effective drugs.
What Are the Benefits of Using Anti-Inflammatory Drugs?
The benefits of using anti-inflammatory drugs in treating laminitis include:
- Pain Relief: NSAIDs effectively reduce pain, improving the animal’s comfort.
- Reduced Inflammation: By inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis, these drugs decrease inflammation in the hoof.
- Improved Blood Flow: Some NSAIDs help relax blood vessels, improving blood flow to the affected area.
- Enhanced Recovery: By managing pain and inflammation, anti-inflammatory drugs support the healing process.
Are There Any Side Effects?
While generally safe, NSAIDs can have side effects, especially with prolonged use or overuse. Potential side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A significant risk with long-term use.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
- Kidney Damage: Prolonged use can affect kidney function.
People Also Ask
How Quickly Do Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Work for Laminitis?
The speed at which anti-inflammatory drugs provide relief can vary. Some improvement may be noticeable within a few hours, but it may take a few days to see significant reduction in pain and inflammation. Consistent administration as prescribed by a veterinarian is essential for optimal results.
Can Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Cure Laminitis?
Anti-inflammatory drugs primarily manage the symptoms of laminitis, such as pain and inflammation, but they do not address the underlying cause. A comprehensive treatment plan, including dietary changes, hoof support, and addressing any underlying conditions, is necessary for a full recovery.
What Else Can Be Used Besides Anti-Inflammatories?
Besides anti-inflammatory drugs, other treatments for laminitis include therapeutic shoeing to support the hoof, dietary management to address metabolic issues, and cryotherapy (cold therapy) to reduce inflammation. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to improve blood flow or realign the hoof structures.
Anti-inflammatory drugs play a vital role in managing the pain and inflammation associated with laminitis, helping to improve the comfort and recovery of affected animals. Remember to consult with a veterinarian for a comprehensive treatment plan.
Want to discover more about the long-term management and prevention of laminitis?