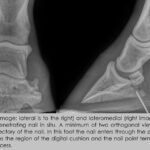
The frog of a horse’s hoof is a crucial component of equine anatomy, acting as a shock absorber and aiding in circulation. Located on the underside of the hoof, it resembles a triangular wedge and plays a vital role in the horse’s overall hoof health and functionality.
What is the Frog of a Horse’s Hoof?
The frog is a V-shaped structure on the underside of a horse’s hoof. It is made of elastic, rubbery material and is situated in the center of the hoof’s sole. The frog functions as a natural shock absorber, helping to cushion the impact of the hoof on the ground. Additionally, it contributes to the horse’s circulation by aiding in the pumping action that facilitates blood flow when the horse moves.
Why is the Frog Important for Hoof Health?
The frog plays multiple roles in maintaining hoof health and overall equine well-being. Here are some of its key functions:
- Shock Absorption: The frog absorbs impact when the horse’s hoof strikes the ground, protecting the internal structures of the hoof.
- Traction: Its rubbery texture helps provide grip, preventing slips and falls, especially on uneven or slippery surfaces.
- Circulation: As part of the horse’s circulatory system, the frog aids in blood flow. When compressed during movement, it helps pump blood back up the leg.
- Protection: The frog acts as a barrier against debris and bacteria, reducing the risk of infections like thrush.
How to Care for a Horse’s Frog
Proper care of the frog is essential for maintaining hoof health. Here are some tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the hooves daily to remove dirt and manure. This prevents bacteria buildup and reduces the risk of infections.
- Trimming: Ensure regular trimming by a professional farrier to maintain the frog’s shape and function.
- Inspect for Thrush: Check for signs of thrush, a common bacterial infection. Look for a foul smell or black discharge, and consult a vet if needed.
- Moisture Balance: Maintain a healthy moisture balance. Too much moisture can lead to softening, while too little can cause cracking.
Common Issues Affecting the Frog
Several issues can affect the frog of a horse’s hoof, impacting hoof health:
- Thrush: A bacterial infection often caused by poor hoof hygiene. It can lead to lameness if untreated.
- Cracks and Tears: These can occur due to over-dry conditions or improper trimming.
- Overgrown Frog: If not trimmed regularly, the frog can become overgrown, affecting the horse’s gait and comfort.
How Does the Frog Compare to Other Hoof Structures?
| Feature | Frog | Hoof Wall | Sole |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Elastic, rubbery | Hard keratin | Tough, fibrous |
| Function | Shock absorption, circulation | Protection, structure | Protection, weight distribution |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning, trimming | Regular trimming | Regular cleaning |
How Can I Ensure My Horse’s Frog Stays Healthy?
To ensure the frog remains healthy, follow these guidelines:
- Schedule Regular Farrier Visits: Routine visits help maintain proper hoof balance and frog condition.
- Monitor Environment: Keep stabling areas clean and dry to prevent bacterial growth.
- Observe Movement: Watch for any signs of discomfort or lameness, which could indicate frog issues.
People Also Ask
What happens if a horse’s frog is damaged?
Damage to the frog can lead to lameness and discomfort. It may also increase the risk of infections like thrush. Prompt treatment and proper care are essential to prevent complications.
How often should a horse’s frog be trimmed?
The frog should be trimmed as part of regular hoof maintenance, typically every 4-8 weeks, depending on the horse’s environment and activity level. A professional farrier can assess and trim the frog as needed.
Can a horse survive without a frog?
While a horse can survive without a fully functional frog, it would significantly impact its mobility and comfort. The frog’s shock-absorbing and circulatory functions are vital for optimal hoof health.
What is thrush in a horse’s frog?
Thrush is a bacterial infection that affects the frog and surrounding areas of the hoof. It is characterized by a foul odor and black discharge. Proper hygiene and treatment are crucial to prevent and manage thrush.
How do I know if my horse’s frog is healthy?
A healthy frog is firm, slightly calloused, and free from foul odors or discharge. Regular inspection and cleaning can help maintain its condition and identify any potential issues early.
Conclusion
The frog of a horse’s hoof is an essential component that plays a significant role in the horse’s overall hoof health and function. Proper care, regular maintenance, and prompt attention to any issues are vital to ensuring that the frog remains healthy. By understanding its functions and addressing any problems promptly, horse owners can help their equine companions maintain optimal hoof health and performance.