Respiratory Issues in Horses: Heaves and Other Conditions

Respiratory health is crucial for horses, especially those involved in athletic activities or living in environments with potential irritants. This article explores common respiratory issues in horses, focusing on heaves and other related conditions, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Understanding Respiratory Issues in Horses

Respiratory problems in horses can range from mild irritations to severe chronic diseases. These issues often affect the horse’s performance, comfort, and overall health.
Common Respiratory Conditions

| Condition | Description | Symptoms | Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heaves (Recurrent Airway Obstruction) | A chronic, non-infectious airway condition similar to asthma in humans. | Coughing, nasal discharge, labored breathing, exercise intolerance | Allergens like dust, mold, pollen, poor ventilation |
| Inflammatory Airway Disease (IAD) | Mild to moderate inflammation of the lower airways, often in young horses. | Coughing, poor performance, mucus in airways | Viral infections, allergens, environmental irritants |
| Pneumonia | Infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. | Fever, cough, nasal discharge, lethargy | Bacterial or viral infections, aspiration |
| Allergic Rhinitis | Inflammation of the nasal passages due to allergens. | Sneezing, nasal discharge, nasal congestion | Pollen, dust mites, mold spores |
Heaves: A Closer Look
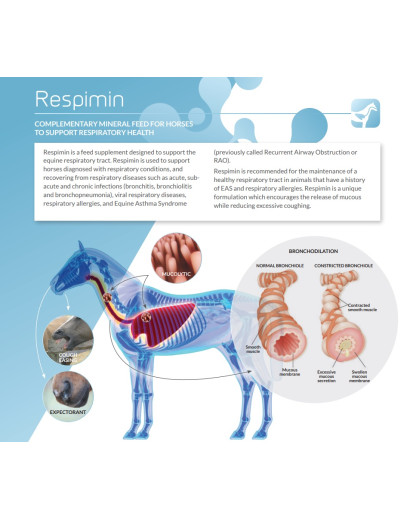
Heaves, also known as Recurrent Airway Obstruction (RAO), is a chronic respiratory condition that significantly impacts a horse’s quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Exposure to airborne allergens such as dust, mold spores, and pollen.
- Poor stable ventilation and dusty bedding materials.
- Genetic predisposition in some horses.
Symptoms
- Chronic cough, especially during or after exercise.
- Difficulty breathing, characterized by an increased respiratory rate and effort.
- Nasal discharge and wheezing sounds.
- Weight loss and decreased performance in severe cases.
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination by a veterinarian.
- Endoscopic evaluation of the airways.
- Bronchoalveolar lavage to analyze airway inflammation.
Treatment and Management
- Reducing exposure to allergens by improving stable hygiene and ventilation.
- Use of corticosteroids and bronchodilators to reduce inflammation and open airways.
- Regular exercise to maintain lung function.
Other Respiratory Conditions
Inflammatory Airway Disease (IAD)
- Often affects young performance horses.
- Symptoms include mild cough and decreased exercise tolerance.
- Managed by reducing exposure to irritants and sometimes medication.
Pneumonia
- Can be life-threatening if untreated.
- Requires prompt veterinary intervention with antibiotics or antifungals.
Allergic Rhinitis
- Causes nasal discomfort and sneezing.
- Managed by minimizing allergen exposure and using antihistamines if necessary.
Prevention Tips
- Maintain clean, dust-free stables with good ventilation.
- Use low-dust bedding materials such as paper or wood pellets.
- Avoid feeding moldy hay; soak hay to reduce dust.
- Regular veterinary check-ups to monitor respiratory health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can heaves be cured?
A1: Heaves is a chronic condition with no cure, but symptoms can be managed effectively with proper care and environmental control.
Q2: How can I tell if my horse has a respiratory problem?
A2: Look for signs like coughing, nasal discharge, labored breathing, and reduced performance.
Q3: Is it safe to exercise a horse with respiratory issues?
A3: Mild cases may tolerate light exercise, but severe symptoms require rest and veterinary advice.
Q4: What are the best bedding options to prevent respiratory issues?
A4: Low-dust options like paper or wood pellets are recommended to minimize airborne irritants.
By understanding and managing respiratory issues such as heaves and other conditions, horse owners can significantly improve their animals’ health and performance. Early detection and proactive care are key to maintaining optimal respiratory function in horses.
