Recognizing Normal vs Abnormal Horse Behavior

Understanding horse behavior is essential for owners, trainers, and enthusiasts to ensure the well-being and safety of these majestic animals. This article explores the key differences between normal and abnormal behaviors in horses, helping you identify signs that indicate health or psychological issues.
Table of Contents

- Introduction to Horse Behavior
- Common Normal Behaviors
- Signs of Abnormal Behavior
- Causes of Abnormal Behavior
- How to Monitor and Respond
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Introduction to Horse Behavior
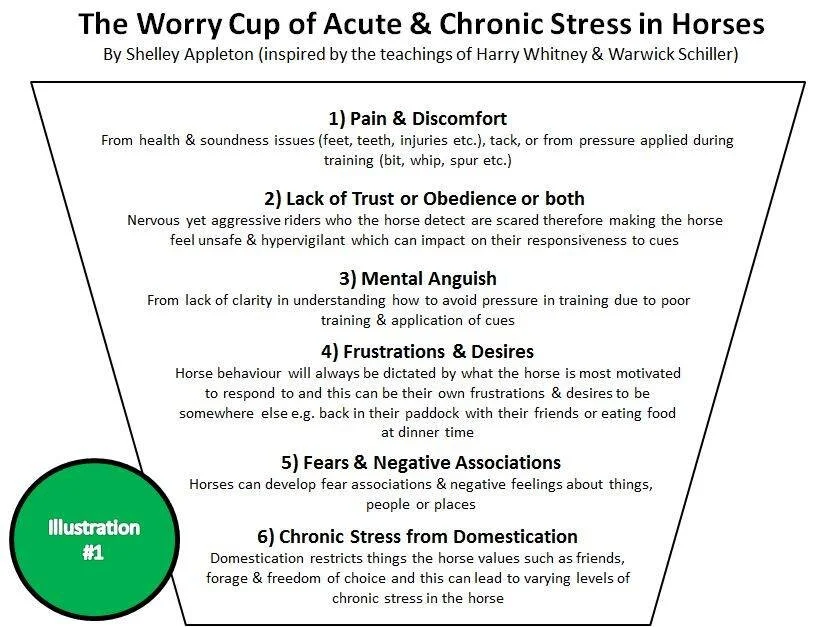
Horses communicate primarily through body language and subtle cues. Recognizing their normal behavior patterns helps in building trust and ensuring their needs are met. Normal behaviors include social interactions, feeding habits, and movement patterns.
2. Common Normal Behaviors
| Behavior | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Grazing | Horses spend a large part of their day eating grass or hay | Nutritional intake |
| Socializing | Interaction with other horses through grooming, play, or vocalizations | Bonding and hierarchy establishment |
| Resting | Standing or lying down to rest and sleep | Physical recovery |
| Movement | Walking, trotting, or cantering around their environment | Exercise and exploration |
3. Signs of Abnormal Behavior
Abnormal behaviors often indicate stress, pain, or illness. Common signs include:
- Pawing or stall walking: Repetitive movements that may signal anxiety or discomfort.
- Excessive biting or kicking: Aggression beyond normal play.
- Head shaking or nodding: Could indicate neurological issues or irritation.
- Loss of appetite or sudden weight loss: Signs of health problems.
- Self-mutilation or cribbing: Harmful behaviors often linked to stress or boredom.
4. Causes of Abnormal Behavior
Understanding the root causes helps in addressing these behaviors effectively:
- Physical pain or injury: Dental problems, lameness, or illness.
- Environmental stressors: Poor living conditions, lack of social interaction.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Imbalanced diet affecting health.
- Psychological factors: Anxiety, fear, or trauma.
5. How to Monitor and Respond
- Regular observation: Keep a daily log of your horse’s behavior.
- Veterinary check-ups: Rule out medical causes.
- Environmental enrichment: Provide toys, social time, and varied activities.
- Professional training: Consult equine behaviorists or trainers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How can I tell if my horse is stressed?
A: Look for signs like excessive sweating, restlessness, changes in eating habits, or abnormal behaviors such as cribbing.
Q2: When should I consult a vet about behavior changes?
A: If abnormal behaviors persist for more than a few days or are accompanied by physical symptoms, seek veterinary advice promptly.
Q3: Can diet affect horse behavior?
A: Yes, nutritional imbalances can lead to irritability or lethargy. Ensure a balanced diet tailored to your horse’s needs.
Q4: Are some abnormal behaviors reversible?
A: Many behaviors can improve with proper care, training, and environmental adjustments.
Recognizing the difference between normal and abnormal horse behavior is crucial for maintaining their health and happiness. By staying attentive and proactive, you can ensure your horse leads a comfortable and fulfilling life.
