Managing Your Horse’s Weight: Overweight and Underweight
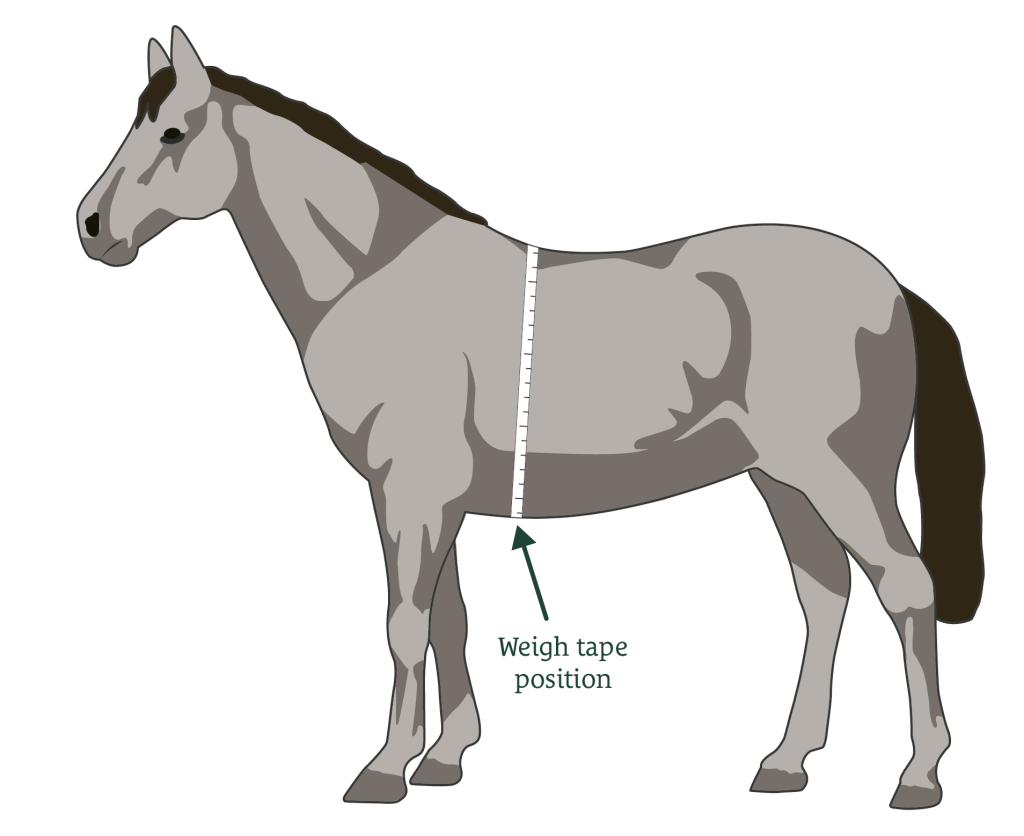
Maintaining an optimal weight for your horse is crucial for its overall health, performance, and longevity. Both overweight and underweight conditions can lead to serious health issues if not addressed properly. This article explores the causes, risks, and management strategies for horses struggling with weight problems.
Understanding Horse Weight

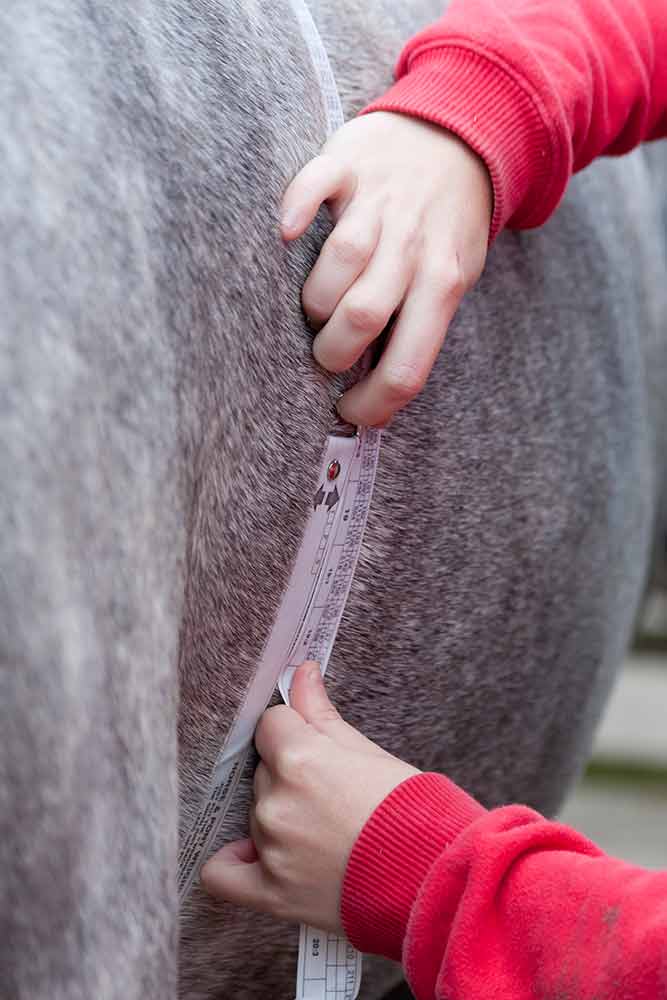
Horses’ ideal weight varies depending on breed, age, activity level, and body condition. Regular monitoring using body condition scoring (BCS) and weight tapes helps track changes effectively.
| Body Condition Score (BCS) | Description | Health Implications |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | Underweight | Risk of malnutrition, weakened immunity |
| 4-6 | Ideal weight | Optimal health and performance |
| 7-9 | Overweight to obese | Increased risk of laminitis, metabolic disorders |
Causes of Weight Issues
Overweight

- Excessive calorie intake, often from rich pasture or high-grain diets
- Lack of sufficient exercise
- Metabolic disorders such as Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS)
- Certain medications or health conditions
Underweight
- Insufficient nutrition or poor-quality feed
- Dental problems affecting chewing
- Parasite infestations
- Chronic illnesses or stress
Risks Associated with Improper Weight
- Overweight horses are prone to laminitis, insulin resistance, joint stress, and decreased stamina.
- Underweight horses may suffer from weakened immune systems, poor coat condition, muscle loss, and reduced energy.
Managing Your Horse’s Weight
For Overweight Horses
- Dietary Adjustments: Reduce calorie intake by limiting grain and rich pasture access.
- Exercise: Implement a consistent exercise routine tailored to your horse’s fitness level.
- Regular Monitoring: Track weight and BCS monthly.
- Veterinary Consultation: Rule out metabolic or hormonal issues.
For Underweight Horses
- Nutritional Support: Provide high-quality forage and consider supplements.
- Dental Care: Ensure teeth are checked and floated regularly.
- Parasite Control: Maintain a deworming schedule.
- Stress Reduction: Minimize environmental and social stressors.
Tools and Techniques
- Weight Tapes: Affordable and easy to use for regular weight checks.
- Body Condition Scoring Charts: Visual guides to assess fat coverage.
- Feed Analysis: Testing forage and feed for nutrient content.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How often should I weigh my horse?
A: Monthly weighing is recommended to monitor trends and adjust care accordingly.
Q2: Can I use human weight scales for my horse?
A: No, horses require specialized scales or weight tapes due to their size.
Q3: What are signs my horse is overweight?
A: Noticeable fat deposits over ribs, neck, and tailhead, and difficulty in movement.
Q4: How can I help an underweight horse gain weight safely?
A: Gradual dietary improvements, dental care, and parasite management are key.
Maintaining your horse’s weight within a healthy range is essential for its well-being. Regular monitoring, proper nutrition, and veterinary care form the foundation of effective weight management.
This article is designed to provide horse owners with practical advice and encourage proactive health management.
